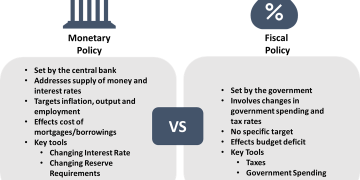
Abstract
Emerging technologies—from artificial intelligence and biotechnology to blockchain and quantum computing—are reshaping the contours of society, the economy, and human experience. This paper examines the transformative role of these technologies across multiple domains, highlighting their capacity to drive economic growth, redefine human interaction, and create new ethical and governance challenges. While emerging technologies offer unprecedented opportunities, they also pose risks of inequality, disruption, and misuse. By analyzing thematic dimensions and real-world case studies, this paper seeks to provide a comprehensive understanding of how emerging technologies are shaping the future.
Introduction
The 21st century has been marked by waves of technological disruption. Emerging technologies are not confined to laboratories or speculative futures—they are already embedded in the daily lives of billions. Smartphones powered by artificial intelligence, genetic sequencing for medical diagnostics, blockchain for financial transactions, and renewable energy innovations for climate resilience are just a few examples of how technological change is influencing society.
This article explores three main questions:
- How do emerging technologies reshape society and human identity?
- What are the economic implications of widespread technological adoption?
- What ethical, cultural, and governance challenges accompany this transformation?
I. Emerging Technologies and Society
1. Artificial Intelligence and Social Life
AI has redefined communication, entertainment, and decision-making. Personalized algorithms on platforms like TikTok and Netflix shape cultural consumption, while generative AI tools assist in education, journalism, and creative arts. However, AI also introduces risks of misinformation, surveillance, and algorithmic bias.
2. Biotechnology and Human Health
Advances in CRISPR gene editing and personalized medicine have revolutionized healthcare. Biotechnology promises cures for genetic diseases and enhanced longevity, but it raises ethical debates about “designer babies,” privacy of genetic data, and the boundaries of human enhancement.
3. Digital Identity and Virtual Worlds
Virtual and augmented reality create new dimensions of human interaction, from gaming communities to workplace collaboration in the metaverse. These experiences blur the line between physical and digital identities, influencing psychology, social norms, and even governance.
II. Economic Impacts of Emerging Technologies
1. Productivity and Innovation
Automation powered by robotics and AI boosts efficiency across industries, from manufacturing to logistics. Quantum computing promises to solve complex optimization problems that today’s computers cannot address, revolutionizing finance, pharmaceuticals, and energy.
2. Disruption of Traditional Sectors
Fintech innovations challenge traditional banking through blockchain and decentralized finance (DeFi). Similarly, renewable energy technologies disrupt fossil fuel industries, reshaping global trade and investment patterns.
3. Inequality and Job Market Shifts
While technology creates new industries and jobs, it also eliminates others. Routine labor in manufacturing and services is increasingly automated, leading to displacement. Without adequate policies, emerging technologies risk widening income inequality and global digital divides.

III. Ethical, Cultural, and Governance Challenges
1. Privacy and Surveillance
Data-driven technologies raise concerns over mass surveillance, data misuse, and erosion of personal privacy. States and corporations wield unprecedented power over citizens through data collection and analysis.
2. Governance and Regulation
Emerging technologies outpace regulatory frameworks. Governments struggle to regulate AI applications, cross-border blockchain systems, and bioengineering without stifling innovation. International coordination remains limited, complicating governance in a globally interconnected world.
3. Cultural Shifts
Technologies influence cultural identity and values. For example, social media fosters global cultural exchange, but also risks homogenization and cultural loss. Meanwhile, the rise of human-machine collaboration redefines concepts of creativity and authorship.
IV. Case Studies
Case Study 1: AI in Healthcare
AI-driven diagnostic tools in radiology and pathology increase accuracy and efficiency. For example, IBM Watson Health has assisted oncologists in treatment recommendations. However, reliance on AI raises accountability questions when errors occur.
Case Study 2: Blockchain and Financial Inclusion
In developing economies, blockchain enables decentralized access to financial services, bypassing traditional banks. Yet, volatility and lack of regulation hinder widespread adoption.
Case Study 3: Renewable Energy Technologies
Solar and wind energy, supported by innovations in battery storage, are transforming energy markets. Countries investing in renewable infrastructure, such as Germany and China, showcase both the economic opportunities and policy challenges of energy transition.
V. Looking Ahead
Emerging technologies will continue to evolve in unpredictable ways. Three scenarios are worth considering:
- Optimistic Future: Equitable access, ethical governance, and global collaboration unlock sustainable growth and human flourishing.
- Pessimistic Future: Widening inequality, technological misuse, and ecological harm create instability and conflict.
- Hybrid Future: A mix of innovation-driven progress and challenges that societies must continually negotiate.
Conclusion
Emerging technologies are not neutral tools; they are active forces reshaping human existence. They hold the potential to redefine society, economy, and human experience in ways that transcend imagination. But their trajectory will depend on how humanity addresses ethical questions, manages risks, and ensures equitable access. The future shaped by emerging technologies is still unwritten—it is up to governments, businesses, and individuals to determine whether this transformation leads to empowerment or division.