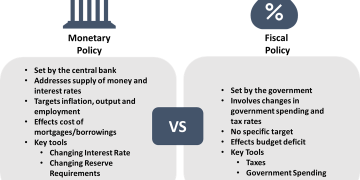
Introduction: Why the Science Matters
The debate about climate change often revolves around policies, economics, or politics, but the foundation of all these discussions lies in climate science.
Understanding the basic mechanisms—greenhouse gases, feedback loops, and tipping points—helps us see why urgent action is required.
1. The Greenhouse Effect: The Planet’s Heat Trap
- Since the Industrial Revolution, atmospheric CO₂ has risen from about 280 ppm to over 420 ppm.
- Greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide trap heat, altering Earth’s energy balance.
- Without this natural effect, Earth would be about 33°C colder, but human activities have strengthened it, causing global warming.
2. Evidence of a Warming World
- Temperature rise: global average has increased by ~1.2°C since pre-industrial times.
- Glacier and ice-sheet loss: Arctic sea ice is shrinking at alarming rates.
- Ocean changes: sea levels have risen ~20 cm since 1900; oceans are also acidifying.
- Extreme weather: increased frequency of heat waves, droughts, wildfires, and intense storms.
3. Climate Feedback Loops
- Albedo effect: as ice melts, darker surfaces absorb more heat, accelerating warming.
- Methane release: thawing permafrost releases methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
- Forest dieback: stressed ecosystems reduce carbon absorption.
These feedbacks mean that warming can speed up once thresholds are crossed.

4. Tipping Points and Irreversibility
Scientists warn that crossing certain limits—like Greenland’s ice-sheet collapse or the shutdown of Atlantic circulation—could set off self-reinforcing changes that are hard or impossible to reverse.
5. The Role of Science in Policy and Action
Scientific models inform global frameworks such as the Paris Agreement and the IPCC assessments.
The message is clear: keeping warming below 1.5–2°C is essential to avoid catastrophic tipping points.
Conclusion
Climate change is not a distant or abstract phenomenon but a physical process governed by well-understood science.
Understanding this science empowers citizens and leaders to make informed decisions for the planet’s future.