I. Introduction
Over the past two decades, urbanization has accelerated at an unprecedented pace, with more than 56% of the global population living in cities. This rapid urban growth has brought significant challenges—traffic congestion, resource depletion, pollution, and unequal access to public services. Enter the Internet of Things (IoT), a technological paradigm that enables interconnected devices to collect, exchange, and analyze data in real time. For smart cities, IoT is not merely a tool but the backbone of a new urban operating system, making cities more efficient, sustainable, and livable.
II. Smart Mobility: The Backbone of Urban Efficiency
Urban mobility has historically been one of the most pressing issues for cities. IoT brings a transformative approach by integrating vehicles, infrastructure, and citizens into a single, intelligent ecosystem.
- Connected Traffic Management: Smart traffic lights that adapt to real-time road conditions can reduce congestion by up to 25%. Sensors embedded in roads and intersections transmit data to centralized systems that adjust signal timing and optimize traffic flow.
- Smart Public Transit: GPS-enabled buses and trains inform passengers about arrival times and delays, improving convenience and reducing waiting times.
- Autonomous Vehicles: IoT facilitates communication between self-driving cars and surrounding infrastructure (V2X communication), which can significantly reduce accidents and fuel consumption.
- Micro-Mobility Solutions: IoT-enabled e-scooters and bikes integrate with city apps, making last-mile travel seamless and environmentally friendly.
III. Intelligent Energy and Resource Management
Smart cities face growing energy demands, but IoT can revolutionize how resources are produced, distributed, and consumed.
- Smart Grids: By connecting meters, sensors, and power plants, IoT allows utilities to balance supply and demand dynamically, reducing waste and lowering costs.
- Water Management: IoT sensors detect pipeline leaks, monitor water quality, and track consumption patterns, enabling conservation and reducing losses.
- Waste Reduction: Connected bins notify collection services when they’re full, improving efficiency and reducing urban clutter.
- Green Building Technologies: Smart thermostats, lighting systems, and energy-monitoring platforms reduce energy consumption in both residential and commercial properties.
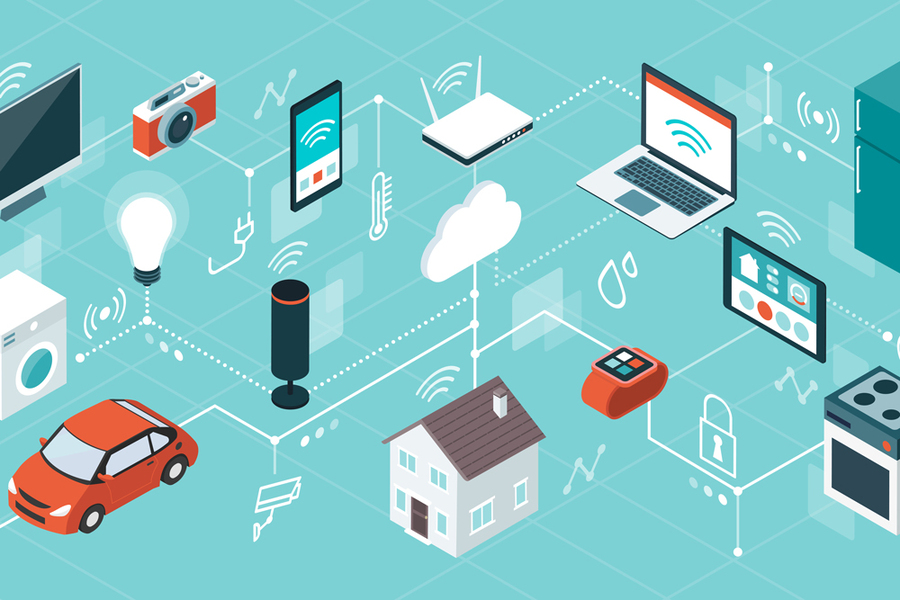

IV. Public Safety and Emergency Response
Urban safety and disaster preparedness are critical priorities. IoT introduces a new paradigm for real-time monitoring and response.
- Connected Surveillance Systems: Smart cameras equipped with AI can detect unusual activity and send instant alerts to law enforcement agencies.
- Disaster Management: IoT-based sensors can predict floods, monitor air quality, and detect seismic activity, giving cities the ability to act before crises escalate.
- Healthcare Integration: IoT-enabled emergency response vehicles share patient data with hospitals en route, saving valuable time during critical incidents.
V. Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its promise, smart city IoT adoption is not without risks.
- Privacy Concerns: The collection of vast amounts of personal data raises questions about who controls and protects that data.
- Cybersecurity Threats: IoT devices often have weak security, making them vulnerable to hacking and potentially jeopardizing entire city systems.
- Equity and Inclusion: High-tech urban environments risk widening the gap between those with access to technology and those without.
- Regulatory Frameworks: Global standards for interoperability and data governance are still evolving.
VI. Conclusion
IoT has the power to transform urban life by making cities more sustainable, efficient, and responsive to human needs. However, realizing this vision requires coordinated investment in technology, robust governance policies, and inclusive design that prioritizes the well-being of all citizens. The smart cities of tomorrow will not merely be technologically advanced but socially cohesive and environmentally conscious.