Introduction
As humanity progresses into the 21st century, the intersection of technology and sustainability will redefine how we live, work, and interact with our environment. From intelligent homes to sustainable cities, the future of human habitats lies in balancing technological innovation with the urgent need to preserve and restore the natural world. This article explores the ways in which technology and sustainability will shape the future of living.
1. The Problem: Current Challenges in Human Living Spaces
At present, human habitats face numerous challenges that threaten both our quality of life and the planet’s health:
- Resource Depletion: Rapid urbanization and industrialization have drained natural resources at an unsustainable rate.
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures, extreme weather, and rising sea levels endanger communities worldwide.
- Pollution: Air, water, and soil pollution from human activity severely affect public health and ecosystems.
- Social Inequality: While some enjoy state-of-the-art living conditions, others face inadequate housing and urban decay.
These problems highlight the need for a paradigm shift in how we design and build human environments.
2. The Solution: Technology and Sustainability as Pillars for Future Habitats
Smart Cities: Efficiency Meets Sustainability
The future of urban living will increasingly revolve around smart cities—high-tech, data-driven environments designed for efficiency, connectivity, and sustainability. Key features include:
- IoT (Internet of Things): Smart devices connected to the internet collect data on everything from energy usage to traffic patterns, optimizing resource distribution and reducing waste.
- Green Infrastructure: Eco-friendly urban planning will incorporate green roofs, sustainable water systems, and energy-efficient buildings to combat climate change.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Cities will increasingly rely on solar, wind, and geothermal energy sources to meet their power demands.
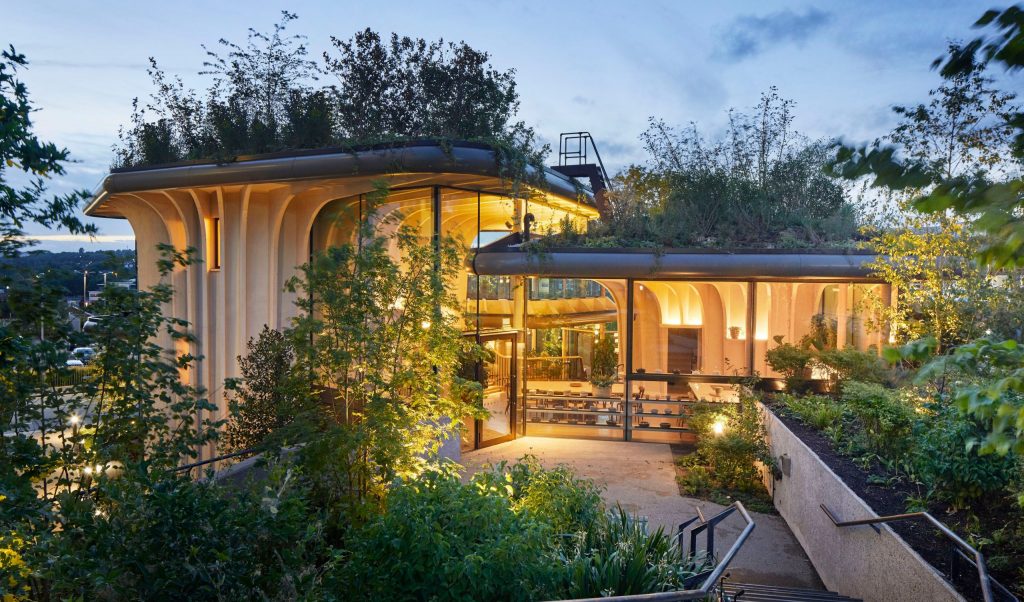

Energy-Efficient Homes and Smart Technologies
Individual homes will also evolve with new technology and design principles:
- Zero-Energy Homes: Homes that produce as much energy as they consume, using solar panels, energy-efficient appliances, and smart home technology.
- AI-Driven Home Automation: AI systems will learn residents’ routines, adjusting lighting, temperature, and security settings to optimize energy use and enhance comfort.
- Sustainable Materials: The future of construction will rely on eco-friendly materials such as bamboo, recycled plastics, and carbon-neutral concrete, reducing the environmental footprint of buildings.
Sustainable Mobility: Eco-Friendly Transportation Solutions
Sustainable transportation will play a crucial role in the future of human living:
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): The widespread adoption of electric cars will reduce dependence on fossil fuels and decrease urban pollution.
- Public Transport 2.0: Autonomous electric buses and trains, as well as shared mobility services, will create more efficient and environmentally friendly transportation networks.
- Bike-Sharing and Walkable Cities: Urban planning will prioritize pedestrian-friendly streets and bike-sharing programs to reduce car usage.
3. Real-World Examples: Successful Models of Future Living
Several cities and initiatives around the world are already laying the groundwork for future living. These examples demonstrate how technology and sustainability can work together to create better habitats:
- Singapore’s Smart Nation Initiative: Singapore is a global leader in implementing smart city technologies, including AI-driven traffic management, smart homes, and sustainable building practices.
- Masdar City, UAE: A zero-carbon city under construction in the United Arab Emirates, Masdar City incorporates renewable energy, smart grid technology, and sustainable urban planning.
- The Crystal, London: One of the world’s greenest buildings, The Crystal serves as a model for energy-efficient, sustainable design, using cutting-edge technologies such as geothermal heating and rainwater harvesting.
Conclusion
The future of living will not simply be a technological utopia but a balance of innovation and sustainability. Smart cities, energy-efficient homes, and sustainable transportation will create environments where technology serves both humanity and the planet. As we move forward, the challenge will be to scale these solutions globally and ensure that the benefits of these advancements reach all corners of society.