Introduction
Trade wars between major global powers have created unprecedented disruptions in global supply chains. With tariffs and trade restrictions making international trade more costly and uncertain, industries around the world have been forced to adapt. The ripple effects extend beyond raw materials and manufactured goods, affecting everything from innovation cycles to business strategies.
This article examines the far-reaching impacts of trade wars on industries, innovation, and global growth, as well as strategies companies are adopting to navigate these challenges.
1. Disruptions in Global Supply Chains
Global supply chains are increasingly interconnected, with components, materials, and products flowing seamlessly between countries. However, the onset of trade wars has disrupted this flow in several ways:
- Tariffs and Taxes: Increased tariffs on imports make it more expensive for companies to procure raw materials or finished goods from other countries.
- Border Delays: Customs checks and border delays increase costs and lead to production downtime.
- Re-shoring and Nearshoring: Companies are bringing production back to their home countries or closer to markets, which increases costs and reduces efficiency.
2. Industry-Specific Impacts: Manufacturing, Technology, and Agriculture
Trade wars have a distinct impact on various industries:
- Manufacturing: Manufacturers that rely on low-cost inputs from abroad are particularly vulnerable to tariffs. Car manufacturers, for example, face higher costs for parts made in China and Mexico.
- Technology: The tech industry is deeply intertwined with global supply chains, with semiconductors, mobile phone parts, and software all being produced across multiple borders. The U.S. sanctions on Chinese tech companies like Huawei have had far-reaching consequences.
- Agriculture: Farmers are hit by tariffs on crops and meats, especially when key markets like China impose retaliatory tariffs on U.S. products.
Each sector faces unique challenges in maintaining operations amidst a global trade war.
3. Innovation and Competitiveness: Surviving and Thriving in Adverse Conditions
Despite the challenges, trade wars are also stimulating innovation:
- Supply Chain Innovation: Companies are exploring more flexible supply chain models that can quickly adapt to disruptions, including the use of AI and blockchain.
- Product Diversification: In response to tariffs, many companies are diversifying their product portfolios and finding new markets for their goods.
- Technological Advancements: The need to reduce reliance on imports is pushing technological innovation in areas such as automation, robotics, and local production capabilities.
Trade wars challenge companies, but they also create new opportunities for innovation and growth.
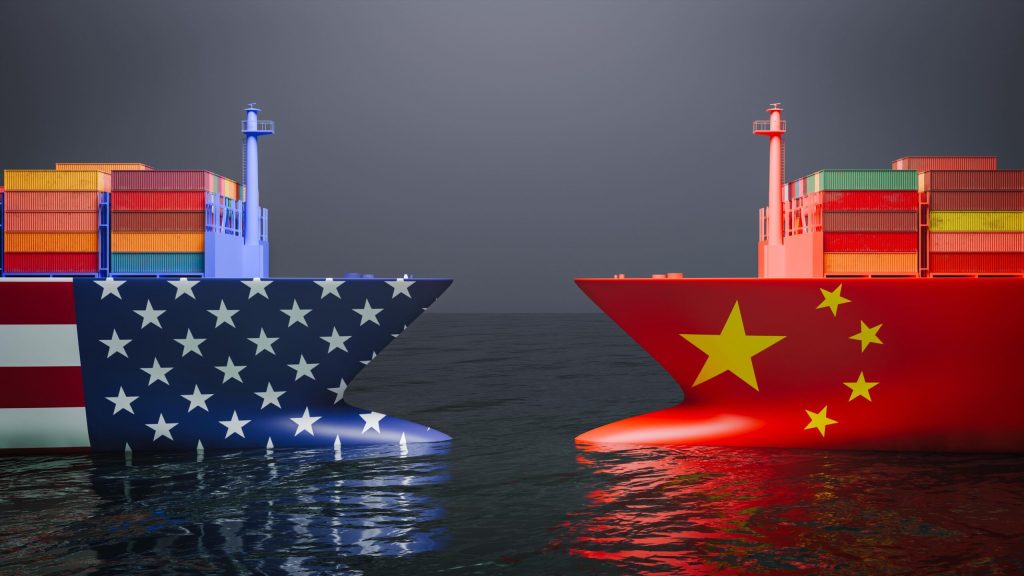

4. Macroeconomic Impact: Slower Growth and Reduced Investment
While industries struggle with the immediate costs of trade wars, broader macroeconomic consequences are becoming apparent:
- Slower Global Growth: Increased trade barriers slow down the global economy, reducing consumer demand and investment.
- Investment Reluctance: Uncertainty surrounding trade policies discourages investment in both developed and developing markets.
- Increased Inflation: Higher production costs due to tariffs are passed on to consumers, leading to inflationary pressures.
5. The Future of Supply Chains: New Strategies and Trends
The future of supply chains is being redefined by trade wars and other global challenges:
- Diversification and Flexibility: Companies are adopting multi-sourcing strategies to avoid over-reliance on a single market.
- Regionalization: Regional trade agreements like RCEP (Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership) and the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) could reduce reliance on global supply chains.
- Digital Supply Chains: Digitalization, including the use of blockchain for transparency, could make supply chains more resilient and efficient.
Conclusion
The ongoing trade wars have permanently altered global supply chains, driving innovation while causing significant economic challenges. Industries must adapt by diversifying their supply sources, investing in technology, and embracing new global partnerships. While trade wars present