Introduction
The 21st-century global economy is marked by unprecedented volatility. Trade tensions, geopolitical rivalries, climate change, technological disruption, and shifting consumer demands have reshaped the market environment in ways that challenge traditional business models.
For companies competing in this dynamic landscape, the ability to navigate uncertainty has become a defining factor of long-term success. This article explores the forces reshaping market environments, the challenges they pose to businesses, and the strategies organizations can adopt to remain resilient and innovative.
1. Forces Driving Changes in the Global Market Environment
1.1 Geopolitical Shifts
The rise of multipolar power structures—driven by the growing influence of emerging economies like China, India, and Brazil—has altered the rules of global trade. Tariff disputes, sanctions, and regional blocs create both risks and new opportunities.
1.2 Technological Disruption
Artificial intelligence, automation, blockchain, and digital platforms have redefined how products are created, delivered, and consumed. These innovations also shorten product life cycles, increasing pressure on businesses to innovate.
1.3 Climate Change and Sustainability Imperatives
As climate risks intensify, governments and consumers demand more sustainable business practices. Companies must invest in renewable energy, low-carbon supply chains, and environmentally responsible production processes.
1.4 Shifting Consumer Behavior
Millennials and Gen Z customers expect transparency, personalization, and ethical production. Their preferences drive trends such as circular economies and digital-first retail experiences.
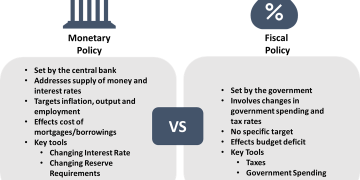
1.5 Financial Market Volatility
Fluctuating interest rates, currency instability, and unpredictable capital flows add complexity to global business strategies, particularly for companies with international supply chains.
2. Key Challenges for Business Strategies
- Strategic Agility:
Companies need to rapidly pivot strategies as market conditions change. Static, long-term plans no longer suffice. - Risk Management:
Uncertainty in supply chains, cybersecurity threats, and geopolitical risks demand more sophisticated risk assessment tools. - Balancing Innovation and Stability:
Firms must invest in disruptive technologies without undermining the stability of existing revenue streams. - Cultural and Regulatory Diversity:
Operating across diverse markets requires adapting to different regulations, cultural preferences, and competitive environments.
3. Adaptation and Innovation Pathways
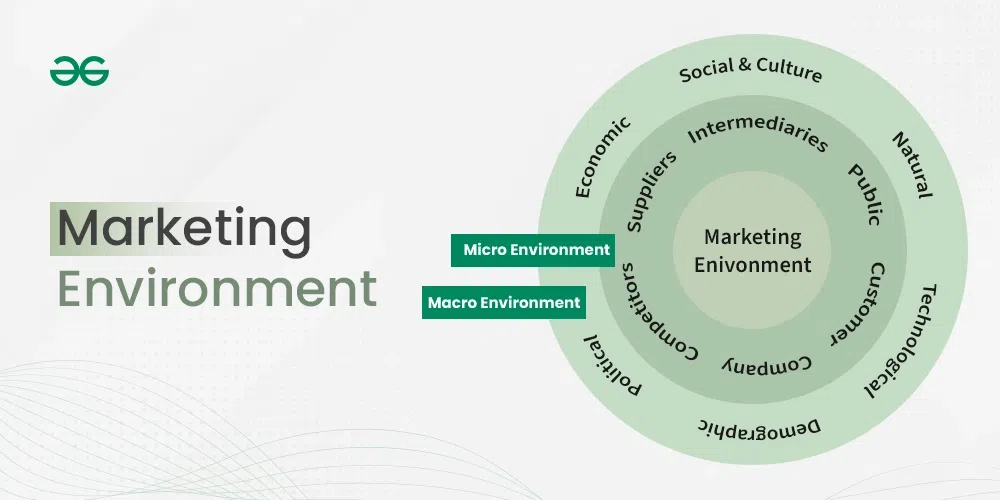
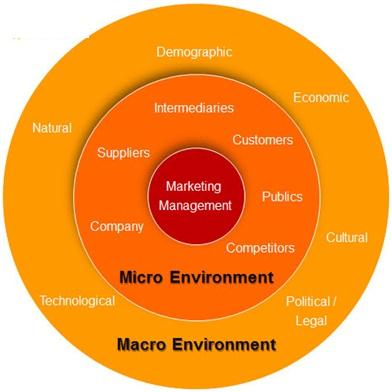
3.1 Digital Transformation
Investing in cloud computing, big data analytics, and AI-driven tools enhances decision-making and operational efficiency.
3.2 Diversification of Supply Chains
Companies are shifting production from single-source locations to multi-regional networks to reduce geopolitical and logistical risks.
3.3 Sustainable Business Models
Integrating ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) practices into strategy builds trust with stakeholders and attracts long-term investment.
3.4 Workforce Reskilling
As automation reshapes jobs, companies must invest in employee reskilling to maintain productivity and foster innovation.
3.5 Strategic Partnerships
Collaborations with startups, research institutions, and even competitors can unlock new markets and technologies.
4. Case Studies in Navigating Market Shifts
4.1 Apple: Managing Supply Chain Volatility
Apple has diversified its manufacturing network beyond China to reduce geopolitical risk, showcasing proactive supply chain management.
4.2 Unilever: Leading with Sustainability
Unilever’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions and sourcing sustainable materials has strengthened its brand resilience amid changing consumer expectations.
4.3 Tesla: Disrupting Traditional Markets
Tesla leveraged innovation in electric vehicles and renewable energy storage to redefine the automotive market and capitalize on climate-conscious policies.
4.4 Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs)
Many SMEs use digital platforms and niche targeting strategies to remain competitive despite resource constraints, proving agility can be an advantage in uncertain markets.
5. Future Trends in Market Environments
- Geoeconomic Fragmentation:
Regional trade blocs may increasingly replace the integrated global market, requiring localized strategies. - Decarbonization-Driven Competition:
Companies leading in low-carbon technologies will gain a strategic edge as governments intensify climate policies. - AI-Powered Decision-Making:
Predictive analytics will allow businesses to anticipate demand shifts, manage risks, and optimize pricing in volatile conditions. - Rise of Ethical Consumers:
Brands prioritizing transparency, inclusivity, and social responsibility will see stronger customer loyalty.
6. Strategic Recommendations for Businesses
- Embrace Scenario Planning:
Prepare for multiple potential futures to enhance resilience against unexpected disruptions. - Invest in Technological Infrastructure:
Prioritize data-driven insights and automation to increase agility and cost efficiency. - Enhance ESG Integration:
Align business goals with sustainability targets to reduce regulatory risks and meet stakeholder expectations. - Strengthen Global-Local Balance:
Develop flexible strategies that allow adaptation to both global trends and local market demands. - Foster Collaborative Ecosystems:
Build alliances across industries to share risks and innovate more effectively.
Conclusion
The modern market environment is defined by uncertainty, complexity, and rapid change. For businesses, success depends on more than just efficiency—it requires adaptability, foresight, and a willingness to embrace innovation.
Organizations that view shifting market environments not as threats but as opportunities for transformation will be better positioned to thrive. By combining strategic agility, technological innovation, and a commitment to sustainable practices, companies can navigate uncertainty and build resilience in an ever-changing global economy.