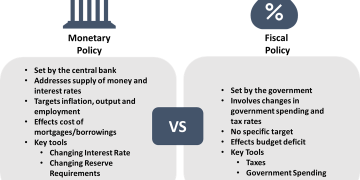
Introduction: The AI Crossroads
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has moved from the realm of science fiction into everyday life. It powers digital assistants, financial algorithms, medical diagnostics, and even creative processes. Yet, as AI scales, humanity faces a crucial question: how to balance the drive for innovation with the demands of ethics and the weight of global consequences.
This essay explores AI at its crossroads, analyzing three interconnected dimensions: technological innovation, ethical responsibility, and geopolitical impact.
1. Innovation: The Engine Driving AI Forward
1.1 Breakthroughs in Machine Learning
- Deep learning and neural networks have transformed computer vision, natural language processing, and robotics.
- Generative AI creates art, music, and text, sparking a new wave of creativity.
1.2 AI as an Economic Driver
- AI adoption could add trillions of dollars to the global economy by 2030.
- Automation improves efficiency across sectors, from logistics to finance.
1.3 The Innovation Imperative
- Nations and corporations race to harness AI for competitive advantage.
- Research funding and venture capital flow disproportionately into AI startups and labs.
2. Ethics: Navigating Complex Moral Questions
2.1 Bias and Fairness
- Algorithms trained on biased data risk reinforcing social inequalities.
- Cases: AI in recruitment or facial recognition showing racial and gender bias.
2.2 Privacy and Surveillance
- AI enables mass surveillance by governments and corporations.
- Raises concerns over civil liberties and human rights.
2.3 Autonomy and Responsibility
- Who is accountable when an AI system causes harm—developers, users, or the machine itself?
- Self-driving car accidents highlight unresolved accountability dilemmas.
2.4 The Ethics of Creativity
- Should AI-generated works be considered original?
- Copyright laws lag behind technological capabilities.

3. Global Impact: AI as a Geopolitical Force
3.1 AI and Global Power Competition
- U.S. and China dominate AI development, shaping future global influence.
- Smaller nations risk dependency on foreign AI technologies.
3.2 Labor Markets and Inequality
- Automation threatens millions of jobs, especially in routine sectors.
- Yet, AI creates new opportunities in data science, robotics, and AI governance.
3.3 AI in Military and Security
- AI-driven drones, cyber tools, and autonomous weapons raise fears of uncontrolled escalation.
- International law struggles to keep pace.
3.4 Environmental Impact
- Training large AI models consumes massive energy resources.
- Sustainable AI becomes an urgent priority.
4. Finding the Balance: Pathways Forward
4.1 Responsible Innovation
- Ethics by design: embedding fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI development.
- Public-private collaboration to establish standards.
4.2 Global Governance
- International agreements on AI, similar to nuclear arms treaties, may be necessary.
- Organizations like the UN and OECD explore AI ethics frameworks.
4.3 Educating Society
- Digital literacy and AI awareness reduce misuse and misunderstanding.
- Workers require retraining for the jobs AI will create.
Conclusion: Standing at the Crossroads
AI represents one of humanity’s most powerful tools, capable of solving global challenges and exacerbating existing inequalities. The path chosen at this crossroads—between innovation, ethics, and global responsibility—will determine whether AI becomes a force for progress or a source of division.
Balancing these dimensions is not optional; it is essential for building a future where AI serves humanity rather than undermining it.